Euro货币
…
ECB Balance Sheet
Key interest rates in the euro area:
- The interest rate on the main refinancing operations (MRO), provide the bulk of liquidity to the banking system.
- the rate on the deposit facility, which banks may use to make overnight deposits with the Eurosystem.
- the rate on the marginal lending facility, which offers overnight credit to banks from the Eurosystem.
在2006之前,ECB的balance sheet占比欧元区GDP约稳定为12%。资产端的活动一是和银行系统的借贷活动,二是投资组合。通常银行面对特殊流动性风险可以通过银行间市场或者准备金通道获得流动性,欧元区银行则通过main refinancing operations,deposit facility和marginal lendign facility获得流动性。负债端可以分为两类:liabilities to credit institutions和autonomous factors. 前者是主要构成,在这一时期约占欧元区GDP的2%。
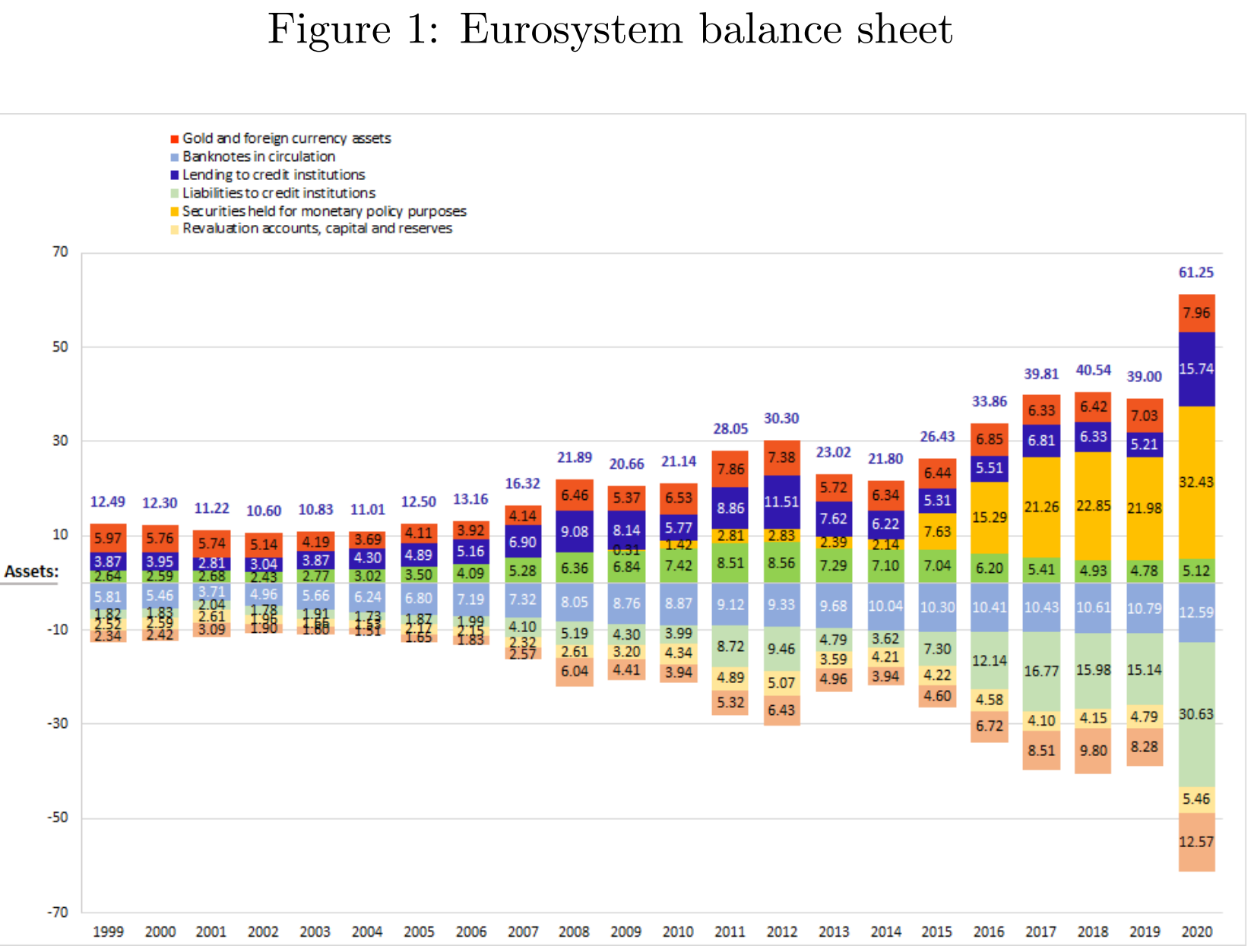
2007-2014期间,资产负债表几乎扩张两倍,在2008占比欧元区GDP达到22%,在危机的初始阶段,货币政策主要针对银行间系统,发挥央行最后贷款人的作用,防止从金融系统溢出对实体经济造成更多伤害。之后的阶段,ECB干预延伸到银行系统之外,除了refinancing operations外,还包括purchases of private assets。
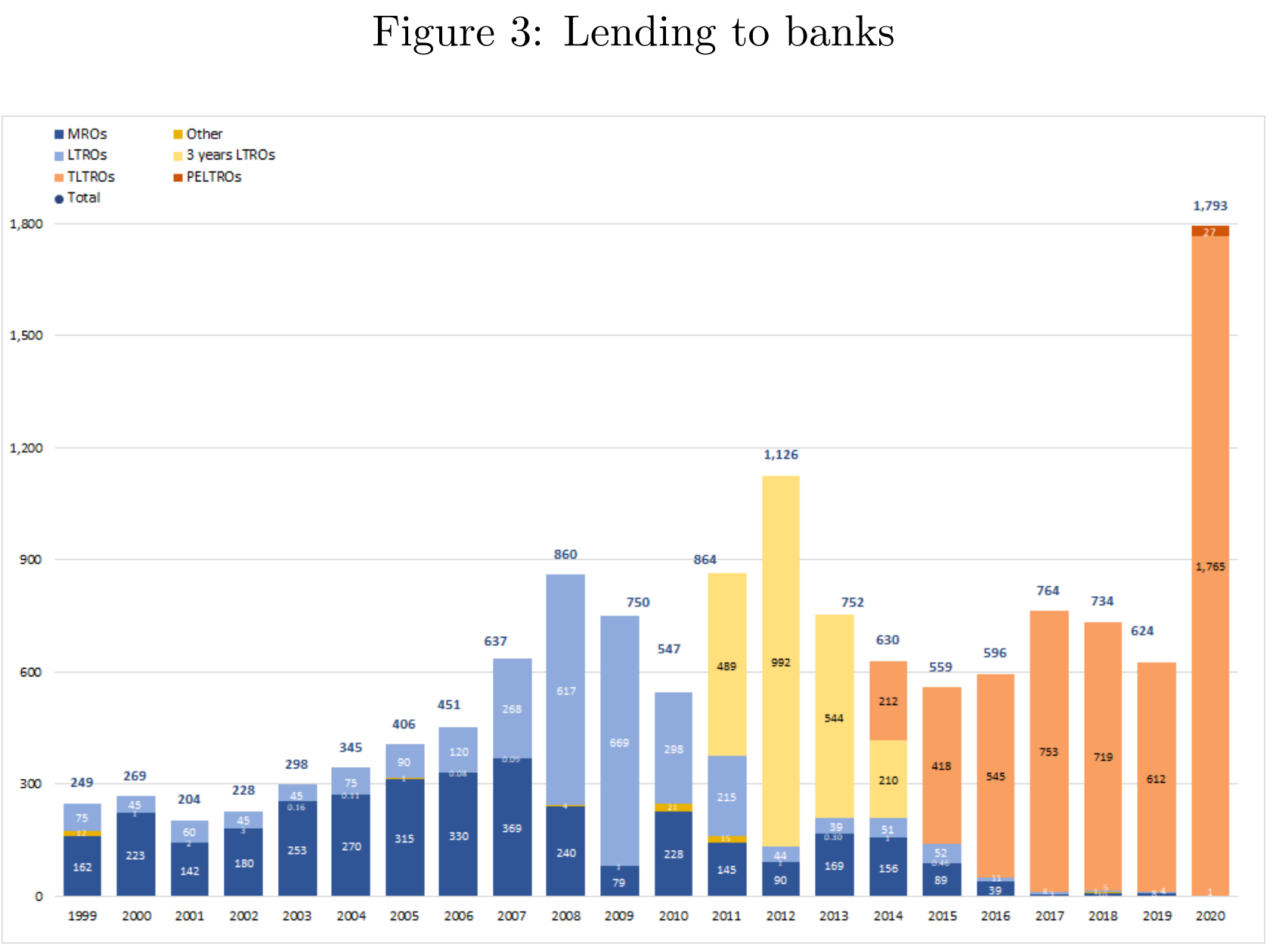
- LTROs: 3-month and later 6-month, almost 7% of GDP in 2007. 2009 started 1-year, 2011 introduced 3-year, over 11% of GDP in 2012.
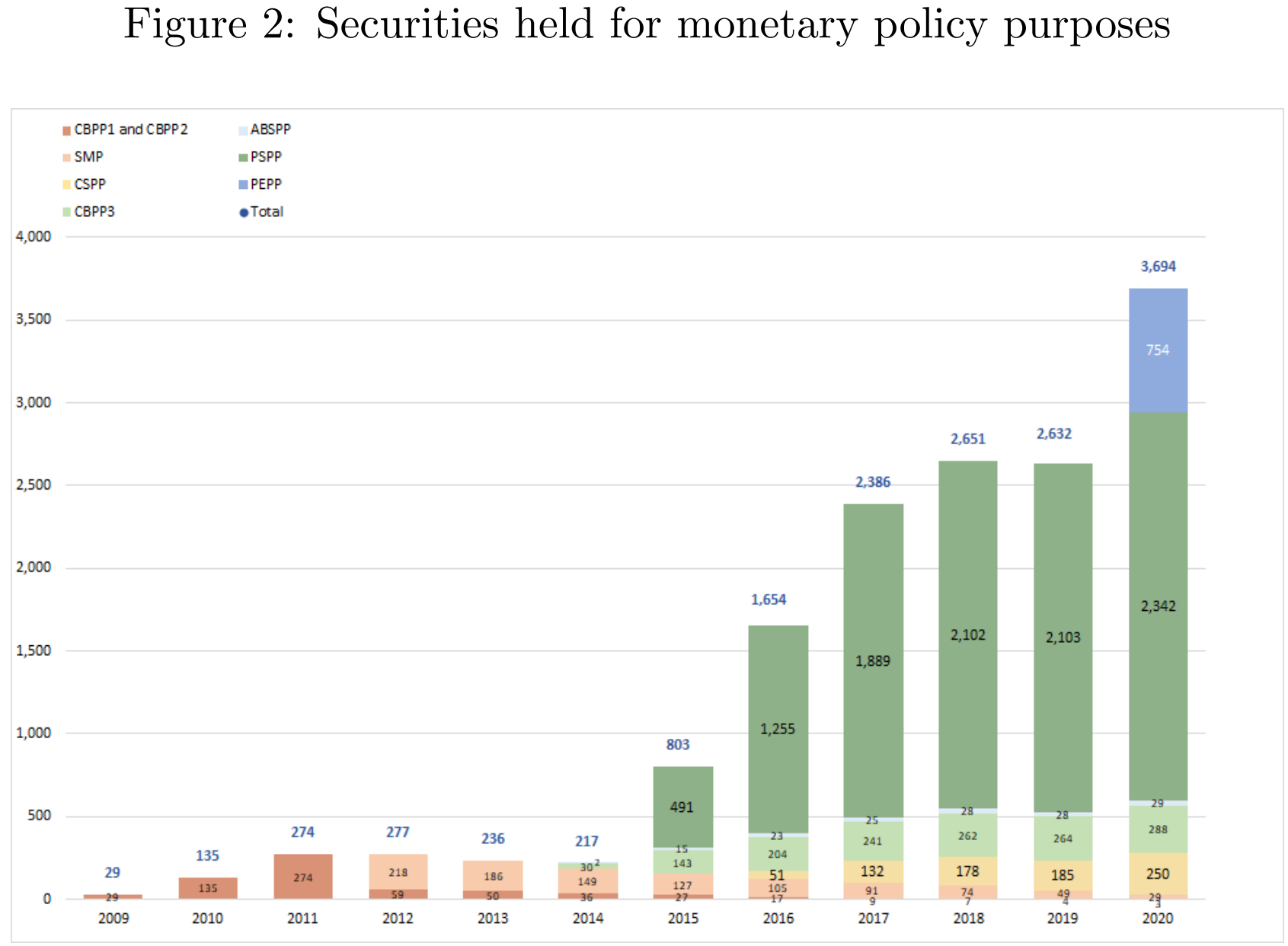
- Covered Bond Purchase Programmes(CBPPs) and Securities Markets Programme(SMP)
2004之后,资产负债表开始激增。ECB除了降低关键利率以外,还推出新的TLTROs和新一轮资产购买计划。
- ABS purchase programme(ABSPP) and Corporate sector purchase programme(CSPP)
- Public sector purchase progeamme(PSPP): launched in 2015, 32% of GDP in 2020.
- The pandemic emergency purchase programme(PEPP)
- Trageted longer-term refinancing operations(TLTROs) and pandemic emergency longer-term refinancing operations(PELTROs)
欧央行货币政策历史
目标:维持价格稳定,中期内HICP年增长率目标水平为2%
传统货币政策工具
- 最低准备金制度
- 中央银行货币互换
- OMO
- 主要再融资操作MRO:提供为期1周的资金
- 长期再融资操作LTRO:提供3M/6M/1Y的资金
- 微调操作FTO
- 常备便利(金融机构发起
- 边际借贷便利MLF:以合格抵押品获取隔夜流动性
- 存款便利DF:存入隔夜存款并获得利息
非常规货币政策工具
- QE
- 前瞻性指引
- 负利率
- 定向长期再融资操作TLTRO
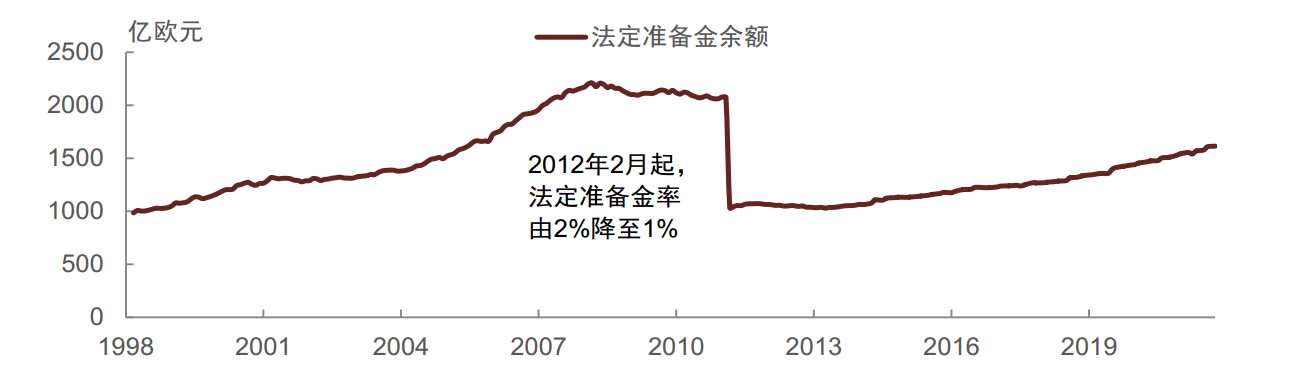
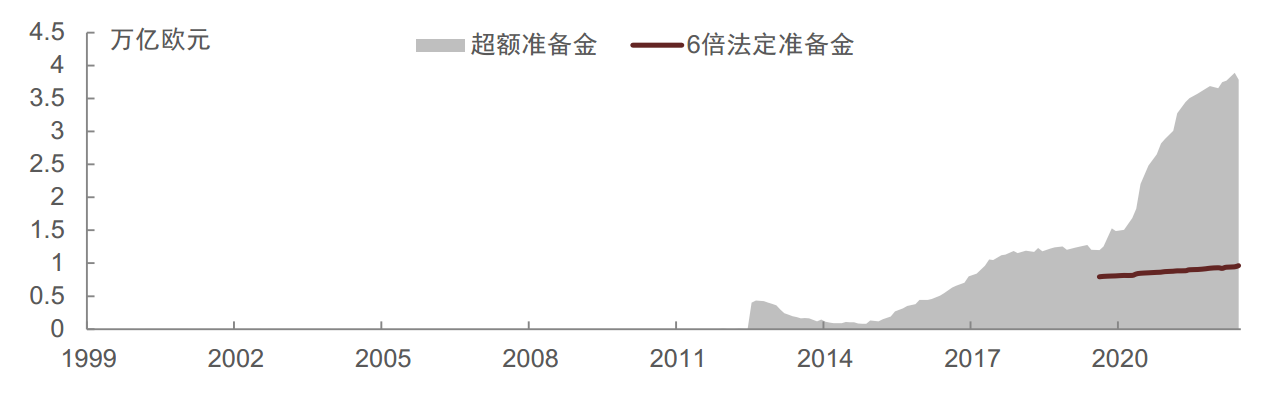
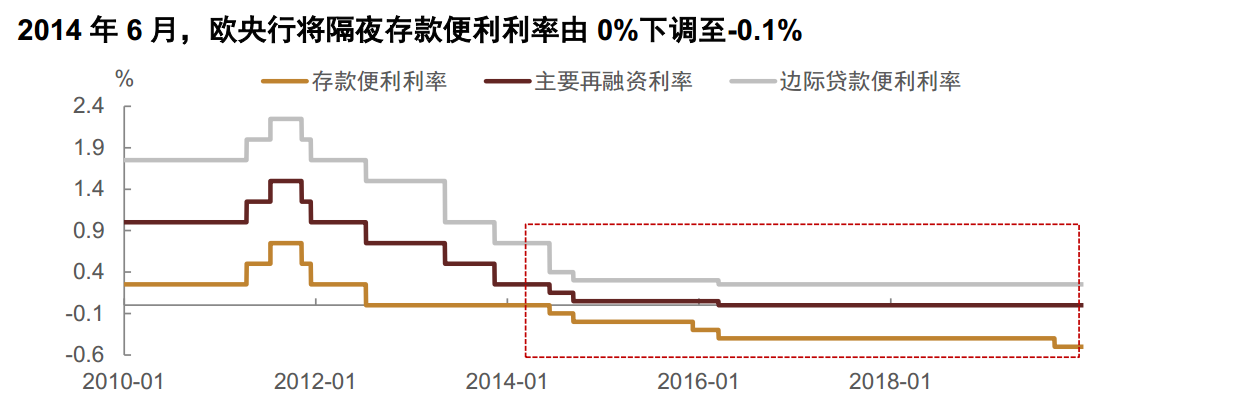
- 超额准备金利率为0% 和DF 孰低,2022年7月DF重新上调至0%后,目前超额准备金利率是0%
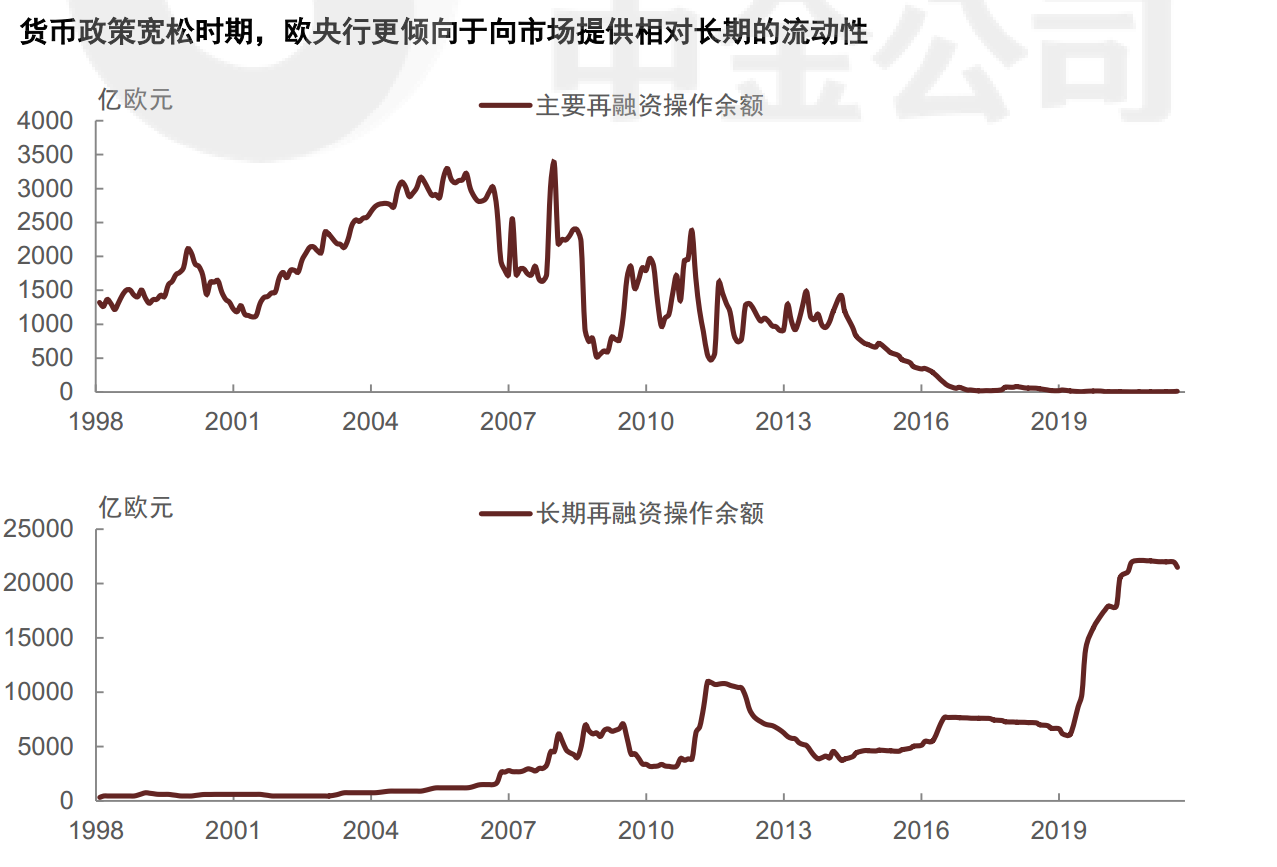
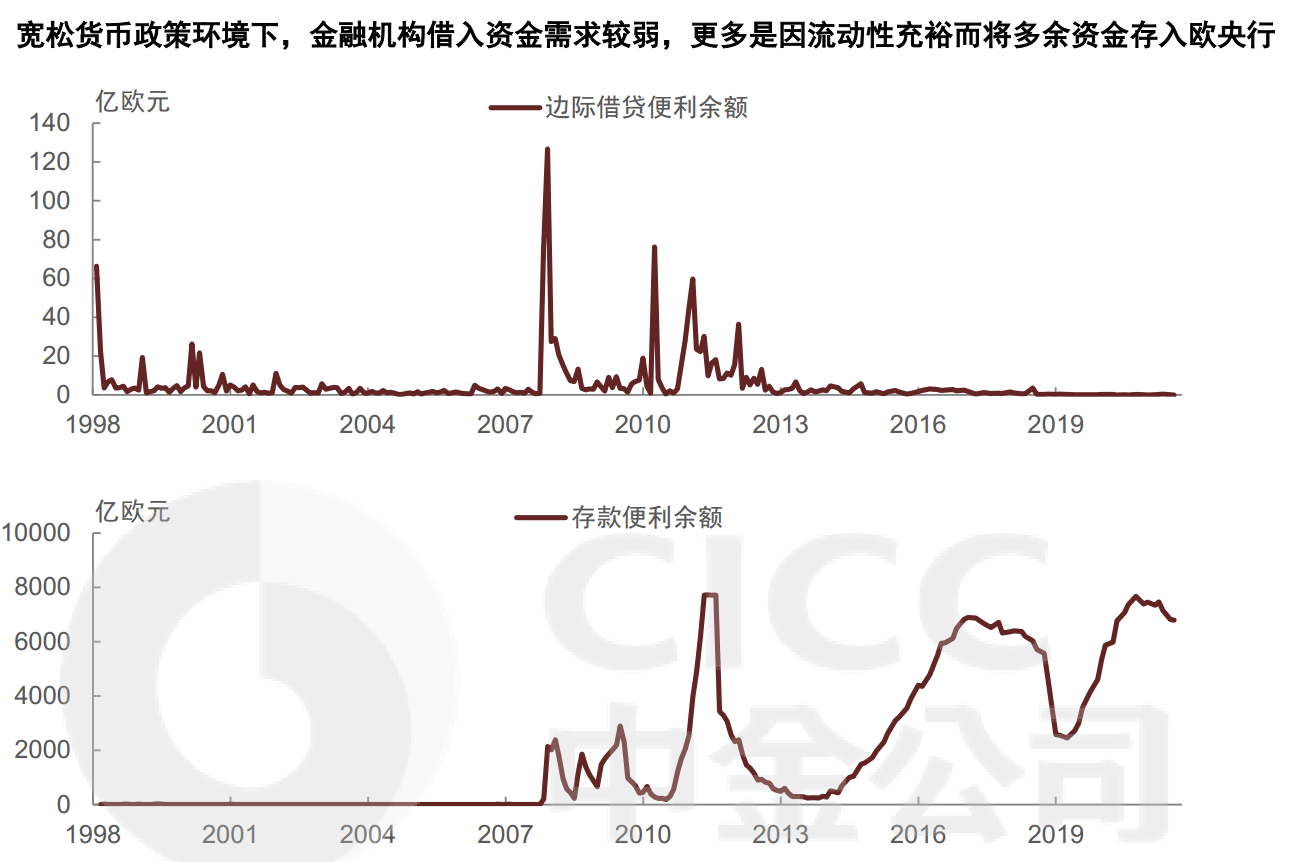
- 2014年6月,将DF由0%下调至-0.1%,进入负利率时代; 2022年7月,加息结束了负利率